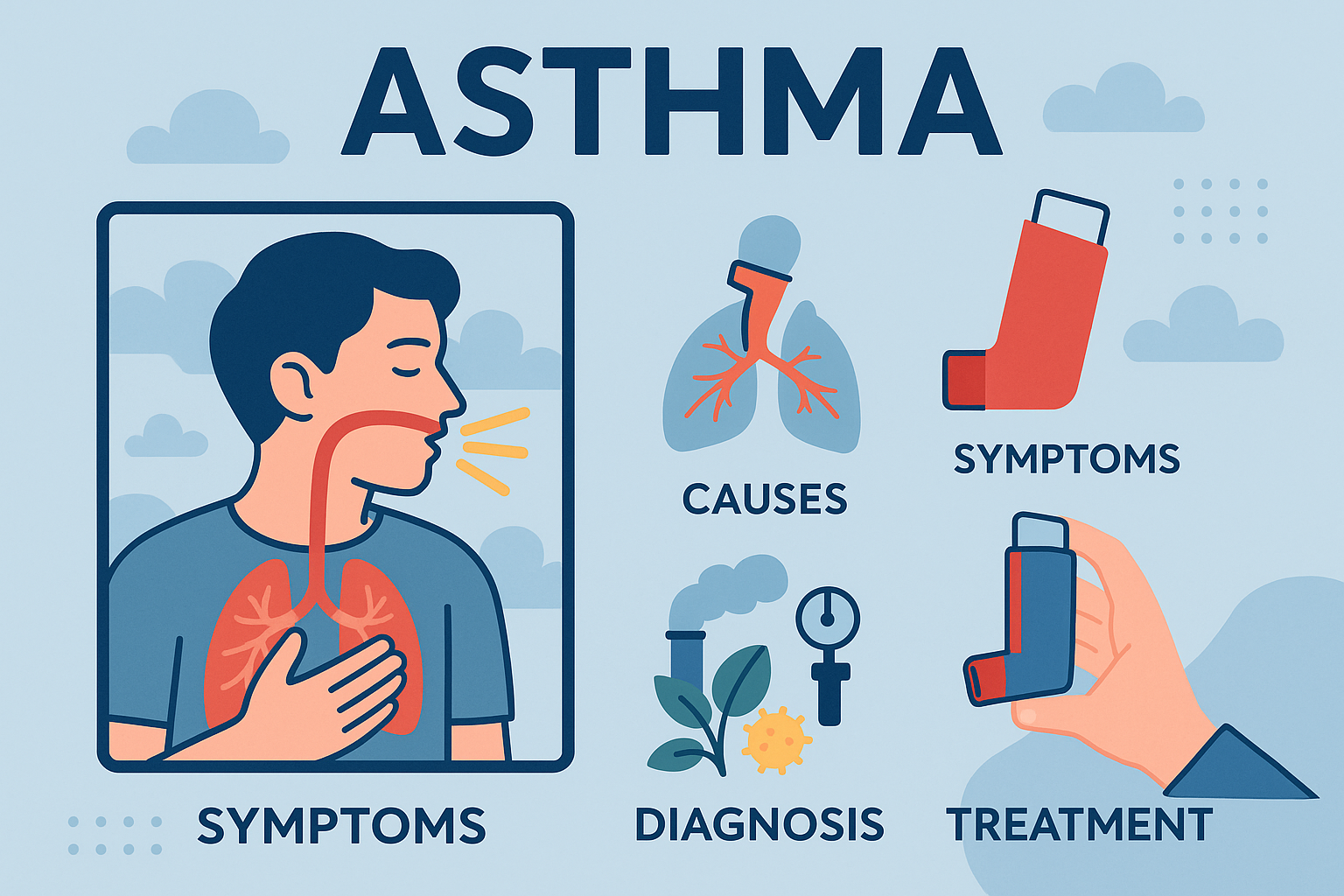
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult for air to flow in and out of the lungs. This inflammation leads to recurrent episodes of coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Although it can develop at any age, asthma often begins in childhood and may persist throughout life. Fortunately, with proper treatment, most people with asthma can live a normal and active life.
How Asthma Affects the Lungs and Respiratory System
Under normal conditions, air flows freely through the bronchi to the lungs. However, in a person with asthma, the airways become hypersensitive.
When exposed to triggers (such as dust, smoke, or exercise), the muscles around the bronchi contract, the airway walls become inflamed, and excess mucus is produced. Together, these reactions cause the breathing difficulty typical of asthma.
Main Causes of Asthma
Asthma does not have a single cause. It results from a complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
People with a family history of asthma or allergies are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Research shows that certain genes linked to immune response play a role in asthma susceptibility.
Environmental Factors and Pollution
Exposure to air pollution, tobacco smoke, industrial chemicals, and other airborne particles can irritate the airways and worsen asthma symptoms. In cities with high pollution levels, asthma is notably more common.
Common Allergies and Sensitivities
Dust mites, pollen, mold, and pet dander are frequent asthma triggers. Individuals allergic to these substances often experience more severe symptoms during specific seasons of the year.
Most Common Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms vary in severity, but the most common include:
- Shortness of breath
- Persistent coughing, especially at night
- Wheezing or whistling sounds while breathing
- Chest tightness or pressure
Mild, Moderate, and Severe Symptoms
- Mild: Occasional cough, no limitations on activities.
- Moderate: Frequent need for a rescue inhaler.
- Severe: Shortness of breath even at rest — a medical emergency.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if you have persistent coughing, difficulty breathing during exercise, or if your inhaler is no longer effective.
A severe asthma attack requires immediate medical attention.
Factors That Aggravate Asthma
Asthma can worsen due to several triggering or aggravating factors, which differ among patients. Recognizing these is key to preventing attacks and maintaining control.
Physical Exercise and Excessive Effort
Exercise-induced asthma is common. Intense physical activity, especially in cold or dry environments, can lead to shortness of breath and coughing.
👉 Tip: Warm up before exercising, avoid extreme weather, and use your preventive inhaler as directed by your doctor.
Climate Changes and Seasonal Variations
Cold, humidity, or sudden temperature changes can irritate the airways. During spring, when pollen levels are high, asthma flare-ups are more frequent.
Wearing a mask outdoors and keeping windows closed on high-pollen days can reduce symptoms.
Emotional Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress can also trigger or worsen asthma attacks. Intense emotions alter breathing patterns, leading to shortness of breath.
Practicing relaxation techniques, deep breathing, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle help control asthma effectively.
Asthma Diagnosis
Diagnosing asthma involves a comprehensive medical evaluation, including a patient’s history, physical examination, and lung function tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor reviews your symptoms, how often they occur, and whether there’s a family history of allergies or asthma.
During the examination, the doctor may detect wheezing or abnormal lung sounds.
Respiratory Tests: Spirometry and Peak Flow Measurement
Spirometry is the most common test for diagnosing asthma. It measures how much air a person can exhale and how fast.
The Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) meter helps patients monitor asthma control at home.
Differential Diagnosis
Asthma symptoms can resemble those of other respiratory conditions, such as chronic bronchitis, COPD, or even heart failure.
A precise medical evaluation is essential to rule out other diseases.
Common Treatments for Asthma
Although there is no permanent cure for asthma, current treatments can control it effectively and minimize symptoms.
Rescue and Controller Inhalers
Rescue inhalers (like albuterol) work quickly during an asthma attack by relaxing airway muscles.
Controller inhalers (with corticosteroids or combination therapies) reduce long-term inflammation and prevent attacks.
Long-Term Maintenance Treatments
These include inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting bronchodilators.
They should be used consistently, even when no symptoms are present, to maintain control over asthma.
Complementary Therapies and Healthy Habits
Besides medication, the following measures are recommended:
- Avoid tobacco smoke.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Engage in moderate, supervised exercise.
- Practice breathing techniques (such as Buteyko or yoga).
⚕️ Important: Never stop or change your medication without consulting your doctor. Asthma treatment must always be personalized.
Prevention and Daily Asthma Control
Prevention is essential for reducing asthma attacks and improving quality of life.
Avoiding Common Triggers
- Clean and ventilate your home regularly to reduce dust and mold.
- Use anti-dust mite covers on pillows and mattresses.
- Avoid air fresheners, strong perfumes, and harsh cleaning products.
- Keep pets out of your bedroom if you’re allergic.
- Do not smoke or allow others to smoke near you.
Proper Use of Inhalers and Devices
A common issue among patients is incorrect inhaler use. To ensure the medication reaches your lungs, always follow your doctor’s or pharmacist’s instructions.
Sometimes, using a spacer device can make inhalation easier and more effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Asthma
1. Can asthma be cured?
No, asthma cannot be cured permanently, but it can be effectively controlled with the right treatment. Many people live symptom-free for years.
2. Can asthma develop in adulthood?
Yes. Although it’s more common in children, asthma can first appear in adults, especially after exposure to allergens or pollutants.
3. Can I exercise if I have asthma?
Yes, as long as your asthma is well controlled. Sports like swimming or cycling are excellent options. Ask your doctor how to adjust your treatment before exercising.
4. What should I do during an asthma attack?
Use your rescue inhaler immediately. If symptoms don’t improve or worsen, seek emergency medical care right away.
5. Does weather affect asthma?
Yes. Cold, humidity, and sudden temperature changes can worsen symptoms. Dress appropriately and avoid very cold environments.
6. Can children outgrow asthma?
In some cases, symptoms decrease as children grow, but asthma may reappear later in life. Regular medical follow-ups are essential.
Conclusion: Living Well with Asthma Is Possible
Although asthma is a chronic condition, it can be managed successfully with proper diagnosis, treatment, and lifestyle adjustments.
With education, discipline, and medical guidance, patients can lead full, active lives without being limited by their condition.
If you or a loved one has asthma, remember: knowledge and prevention are your strongest allies.
🔗 External Reference:
World Health Organization – Asthma
Articles that may interest you:
